The Iron Curtain that once divided Europe may be long gone, but the continent today is split by stark differences in public attitudes toward religion, minorities and social issues such as gay marriage and legal abortion. Compared with Western Europeans, fewer Central and Eastern Europeans would welcome Muslims or Jews into their families or neighborhoods, extend the right of marriage to gay or lesbian couples or broaden the definition of national identity to include people born outside their country.
These differences emerge from a series of surveys conducted by Pew Research Center between 2015 and 2017 among nearly 56,000 adults (ages 18 and older) in 34 Western, Central and Eastern European countries, and they continue to divide the continent more than a decade after the European Union began to expand well beyond its Western European roots to include, among others, the Central European countries of Poland and Hungary, and the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania.
The continental divide in attitudes and values can be extreme in some cases. For example, in nearly every Central and Eastern European country polled, fewer than half of adults say they would be willing to accept Muslims into their family; in nearly every Western European country surveyed, more than half say they would accept a Muslim into their family. A similar divide emerges between Central/Eastern Europe and Western Europe with regard to accepting Jews into one’s family.
In a separate question, Western Europeans also are much more likely than their Central and Eastern European counterparts to say they would accept Muslims in their neighborhoods. For example, 83% of Finns say they would be willing to accept Muslims as neighbors, compared with 55% of Ukrainians. And although the divide is less stark, Western Europeans are more likely to express acceptance toward Jews in their neighborhoods as well.
Attitudes toward religious minorities in the region go hand in hand with differing conceptions of national identity. When they were in the Soviet Union’s sphere of influence, many Central and Eastern European countries officially kept religion out of public life. But today, for most people living in the former Eastern bloc, being Christian (whether Catholic or Orthodox) is an important component of their national identity.
In Western Europe, by contrast, most people don’t feel that religion is a major part of their national identity. In France and the United Kingdom, for example, most say it is not important to be Christian to be truly French or truly British.
To be sure, not every country in Europe neatly falls into this pattern. For example, in the Baltic states of Latvia and Estonia, the vast majority of people say being Christian (specifically Lutheran) is not important to their national identity. Still, relatively few express willingness to accept Muslims as family members or neighbors.
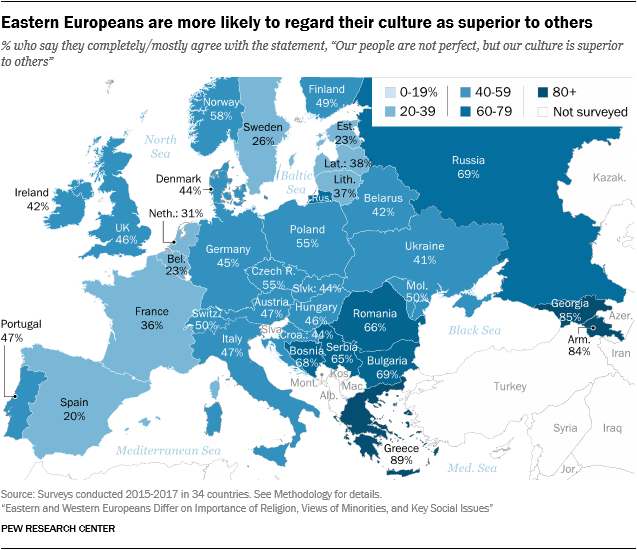
But a general East-West pattern is also apparent on at least one other measure of nationalism: cultural chauvinism. The surveys asked respondents across the continent whether they agree with the statement, “Our people are not perfect, but our culture is superior to others.” While there are exceptions, Central and Eastern Europeans overall are more inclined to say their culture is superior. The eight countries where this attitude is most prevalent are all geographically in the East: Greece, Georgia, Armenia, Bulgaria, Russia, Bosnia, Romania and Serbia.
People in Central and Eastern Europe also are more likely than Western Europeans to say being born in their country and having family background there are important to truly share the national identity (e.g., to be truly Romanian; see here.).
Taken together, these and other questions about national identity, religious minorities and cultural superiority would seem to indicate a European divide, with high levels of religious nationalism in the East and more openness toward multiculturalism in the West. Other questions asked on the survey point to a further East-West “values gap” with respect to key social issues, such as same-sex marriage and legal abortion.
In addition, when it comes to views about Muslims and Jews, young adults in most countries in Central and Eastern Europe are no more accepting than their elders.
Consequently, those in this younger generation in Central and Eastern Europe are much less likely than their peers in Western Europe to express openness to having Muslims or Jews in their families. For example, 36% of Polish adults under 35 say they would be willing to accept Muslims in their family, far below the two-thirds of young French adults who say they would be willing to have Muslims in their family – mirroring the overall publics in those countries.